Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis
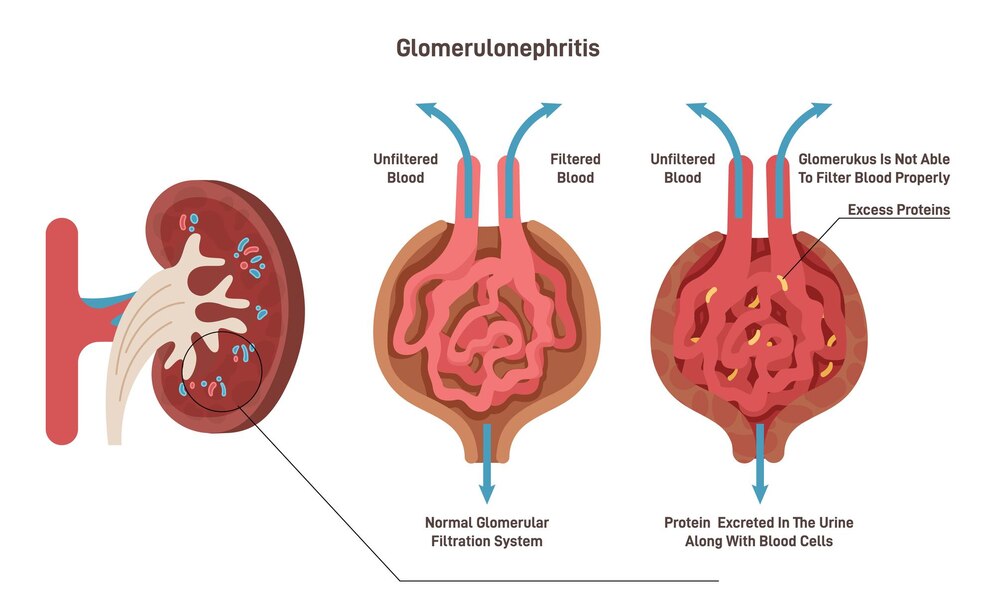
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is a type of glomerulonephritis characterized by a rapid decline in kidney function over days to weeks. It is often associated with severe glomerular injury and can lead to rapidly worsening kidney failure if not promptly diagnosed and treated.
Causes
RPGN can be caused by various underlying conditions, including:
- Immune-Mediated Diseases: Such as anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) disease and immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis (e.g., lupus nephritis).
- Vasculitis: Inflammatory conditions affecting blood vessels, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
- Infections: Post-infectious glomerulonephritis, often following streptococcal infections.
- Systemic Diseases: Such as Goodpasture syndrome and Henoch-Schönlein purpura.
Clinical Presentation
Patients with RPGN typically present with:
- Acute Kidney Injury: Rapid decline in kidney function, often leading to oliguria (reduced urine output).
- Nephritic Syndrome: Hematuria (blood in urine), proteinuria (protein in urine), and hypertension.
- Systemic Symptoms: Such as fatigue, malaise, fever (in infectious causes), and respiratory symptoms (in anti-GBM disease).
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of RPGN involves:
- Kidney Biopsy: Essential for confirming the diagnosis and identifying the underlying cause of glomerular injury.
- Laboratory Tests: Including renal function tests (serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen), urine analysis (hematuria, proteinuria), and serological tests (antibodies, complement levels).
- Imaging: Such as ultrasound or CT scan to assess kidney size and structure.
Treatment
Treatment of RPGN aims to:
- Control Inflammation: High-dose corticosteroids and immunosuppressive medications (e.g., cyclophosphamide, rituximab) to suppress immune-mediated inflammation.
- Manage Complications: Such as hypertension and electrolyte imbalances.
- Supportive Care: Including dialysis for severe kidney failure and management of fluid and electrolyte disturbances.
Prognosis
The prognosis of RPGN depends on the underlying cause, extent of kidney damage, and response to treatment. Early diagnosis and aggressive management are crucial to prevent irreversible kidney injury and improve outcomes.
Patient Education
Dr. Tanish Dhir emphasizes:
- Early Recognition: Educating patients about symptoms of RPGN and the importance of seeking prompt medical attention.
- Compliance: Adherence to prescribed medications and follow-up appointments to monitor kidney function and adjust treatment as needed.
